Imagine turning your everyday farm waste—manure, crop leftovers, even food scraps—into useful energy and a natural fertilizer. That’s exactly what anaerobic digestion does. In this guide, we’ll explain what anaerobic digestion is, how it works, what materials you can use, its benefits for your farm, and some practical, step-by-step advice on setting up your own system. Whether you’re curious about reducing operating costs, generating renewable energy, or producing nutrient-rich fertilizer in an environmentally friendly manner, this guide is for you.
Introduction: Turning Waste into Wealth
Every day, farms produce a lot of organic waste. Traditionally, this waste might be seen as a burden to dispose of. However, nature has its own way of breaking down these materials. Anaerobic digestion is a process that takes advantage of the power of tiny microorganisms. By letting these microorganisms “eat” organic matter in a controlled, oxygen-free environment, the process creates biogas—a clean, renewable source of energy—and digestate, a byproduct that makes an excellent fertilizer.
In simple terms, anaerobic digestion is nature’s recycling process. It not only helps reduce waste and avoid pollution from manure heaps but also turns that waste into something valuable. The energy you produce can be used for cooking, heating, or even powering small farm machinery, and the leftover material enriches your soil. It’s a win-win for your pocket and the planet.
What Exactly Is Anaerobic Digestion?
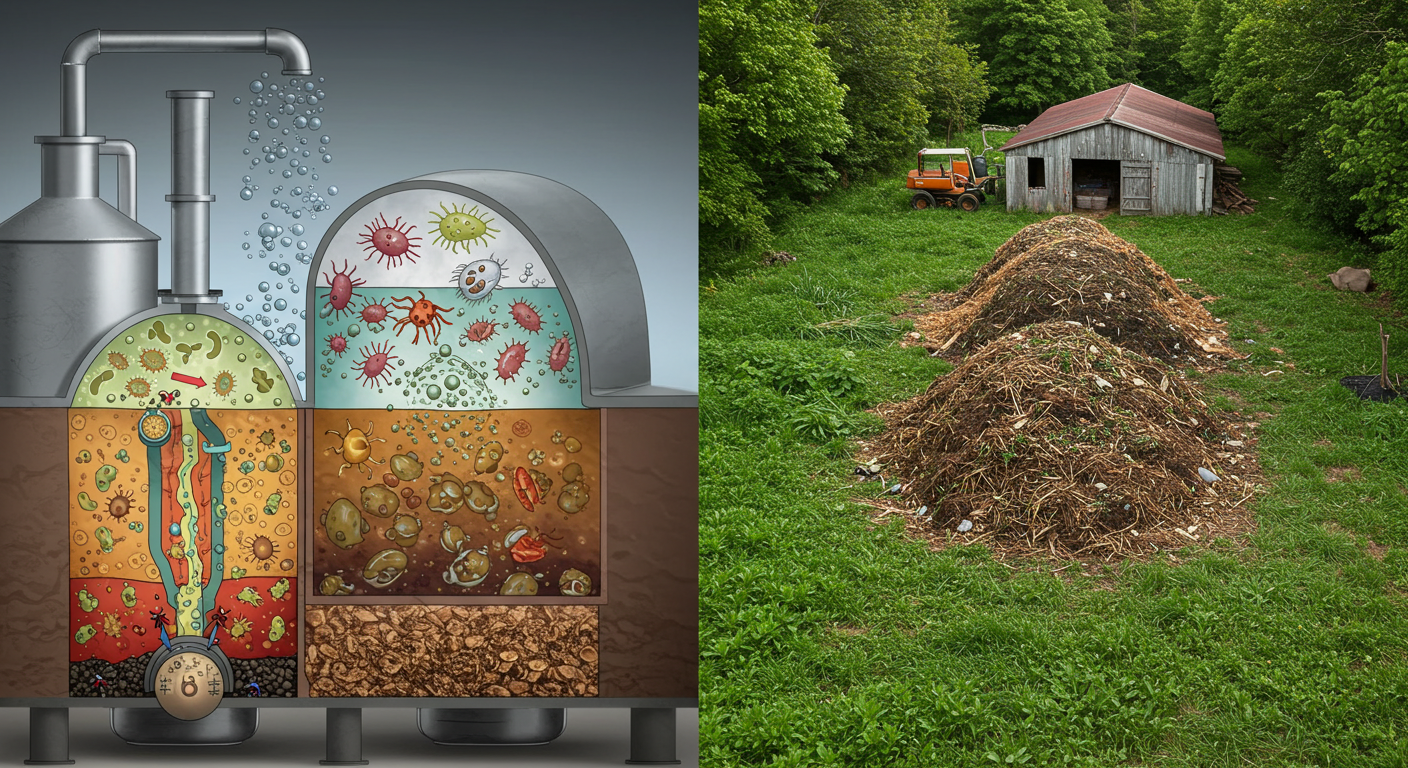
Anaerobic digestion is a natural process that occurs when organic material breaks down without oxygen. “Anaerobic” means “without oxygen,” and “digestion” refers to the breakdown process performed by microorganisms. Inside a sealed tank called a digester, these microorganisms work on materials like animal manure, crop residues, and even food waste. As they break down the organic matter, they produce biogas—a mixture mostly of methane and carbon dioxide—and a nutrient-rich substance called digestate, which is an excellent natural fertilizer for your fields.
You might have noticed that piles of manure or compost can sometimes give off a mild odor while slowly breaking down. What happens in a well-managed digester is very similar—but controlled in a way that you can capture and use the useful parts. This process is not new; it has been observed in nature for centuries and now, many farmers around the world are turning it into a practical solution for energy and waste management.
How Does the Process Work? A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Let’s break down the process into simple, everyday terms:
- Collection and Mixing of Feedstock: Start by gathering organic waste. This could be livestock manure, leftover crops, or even food waste from farm kitchens. These materials are mixed together with water to create a slurry. The water helps the microscopic organisms move around and work more efficiently in the tank.
- The Sealed Digester: The slurry is then stored in an airtight container called a digester. No oxygen is allowed in, which is essential for the anaerobic (oxygen-free) process. In this sealed environment, the microorganisms begin their work.
- Microorganisms at Work: Over a period—often several weeks—the tiny microbes break down the organic matter. As they “digest” the waste, they produce biogas. Think of it like a slow-cooking process where, instead of heat, the action of tiny living creatures transforms your waste into gas and fertilizer.
- Biogas Collection: The biogas produced, which is primarily methane (a useful fuel), is captured at the top of the digester. Depending on the size and setup of your system, you might use this gas directly for heating, powering engines, or cooking. It’s a renewable energy source that can help reduce your reliance on purchased fossil fuels.
- What’s Left: Digestate: After most of the organic material is broken down, the remaining matter—called digestate—is rich in nutrients. This substance can be separated into liquid and solid parts. The liquid part is often used as a great liquid fertilizer, while the solid fraction can be composted or spread directly on the land, helping your crops grow strong and healthy.
This process is natural, but when you control it in a digester, you capture the benefits and make them work for your farm, turning waste into a useful resource.
Materials You Can Use in Anaerobic Digestion
One of the best advantages of anaerobic digestion is its flexibility. Most organic materials can be safely digested. Here are some examples:
- Animal Manure: Manure from cattle, pigs, poultry, and goats is commonly used because it is rich in organic matter and already full of the microbes needed to start the process.
- Crop Residues: Leftover plant material after harvest, such as corn stalks, straw, and even vegetable washings, can work well in the digester.
- Food Waste: Leftover produce or discarded food from on-farm kitchens can be added to the mix. Just remember not to include too much salt or oil, as these can interfere with the process.
- Other Organic Waste: You might also use dairy waste or even certain organic industrial byproducts. The key is ensuring that the materials are free from chemicals that might harm the microorganisms.
When putting together your feedstock, aim for a good mix of “greens” (nitrogen-rich materials like fresh manure or green crop residues) and “browns” (carbon-rich materials like straw or dried leaves). This mix helps create a balanced environment for the microbes.
The Benefits of Anaerobic Digestion on Your Farm
Energy Savings and Independence
Many farms face rising energy costs. By using the biogas produced through anaerobic digestion, you gain an on-farm source of renewable energy. This gas can be used for heating barns, cooking, or even generating electricity with a generator designed for biogas. Over time, the savings on fuel bills can be significant.
Fertilizer That Feeds Your Soil
Instead of buying chemical fertilizers, you can use digestate—a nutrient-rich byproduct—as a natural fertilizer. Digestate contains important nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium that your crops need. Not only does this help reduce fertilizer costs, but it also improves soil health in a more sustainable way, promoting a cycle of natural growth and nutrient recycling.
Waste Management Made Practical
Disposing of farm waste can be a challenge, especially in the face of increasing environmental regulations. Anaerobic digestion helps you manage waste on-site. By turning what might be seen as a nuisance into valuable products, it helps keep your farm clean, reduces odors, and minimizes the risk of water or air pollution from unmanaged waste piles.
Environmental Benefits
Adopting anaerobic digestion is good for the planet. By capturing methane—a greenhouse gas that is far more potent than carbon dioxide—and using it as a renewable energy source, you help significantly lower overall greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, using biogas instead of fossil fuels contributes to a cleaner, greener farm environment.
Community and Economic Advantages
In some areas, farms with anaerobic digestion systems join together to supply biogas or fertilizer to a broader community. This kind of teamwork can lead to stronger local economies, job creation, and shared resources that support more sustainable farming practices overall.
How to Set Up an Anaerobic Digestion System: Step-by-Step for Farmers
Here’s a practical, step-by-step guide to help you understand the basics of setting up an anaerobic digestion system on your farm.
1. Assess Your Farm’s Resources
Action Step:
- List the types and quantities of organic waste your farm produces.
- Evaluate if the waste is steady throughout the year or seasonal.
- Speak with your local agricultural extension office about incentives or expertise available in your area.
By understanding what waste you have available, you can design a system that matches your farm’s needs.
2. Determine the Size and Type of System
Systems can range from small, plug-flow digesters to larger, continuously stirred tank reactors (CSTRs). For many family farms, a modular or smaller digester might be the best starting point.
Action Step:
- Look into various system types by visiting local demonstration projects or speaking with farms that have installed digesters.
- Consider whether you want to start with a small pilot project or invest immediately in a larger system.
3. Build or Purchase the Digester
There are a couple of options here. You can either build a simple biogas digester yourself or purchase a ready-made system. Local suppliers specializing in agricultural technology can be a great resource.
Action Step:
- If you’re building your own, gather materials such as a large airtight tank (this could be a repurposed barrel, a concrete tank, or a purpose-built digester), piping for gas collection, and safety valves.
- Make sure the tank is durable, completely sealed, and has a method for continuously feeding in more waste and extracting the finished digestate.
4. Install the Biogas Collection System
The biogas produced needs to be safely captured and stored. This usually involves a piping system and a gas storage unit or a direct connection to where the gas is used.
Action Step:
- Plan your gas collection layout. The highest part of the digester should have a gas outlet since biogas naturally rises to the top.
- Ensure that all parts of the system are leak-proof. Regular inspections and using recommended fittings and valves are key.
5. Start Feeding Your Digester
Begin with a “startup” phase. Fill the digester with your slurry (a mix of organic waste and water). In the early days, the feed rate should be controlled to allow the microorganisms time to adapt and multiply.
Action Step:
- Mix your feedstock in a way that maintains a balanced ratio of water to solids (often around 8:1 to 12:1 by weight).
- Gradually increase the amount of waste you add. Keep a simple logbook recording feed times, amounts, and any observable changes in gas production.
6. Monitor and Adjust the Process
Anaerobic digestion is sensitive to temperature, pH, and the balance of nutrients. Farmers often notice that a few adjustments lead to a smoother process and higher gas yields.
Action Step:
- Invest in basic monitoring equipment like a thermometer and a pH meter.
- Check the system daily at first, then set a periodic schedule to inspect and record essential parameters.
- Adjust the feed composition or the tank’s temperature as needed. For example, if the gas output drops, it might be a sign the balance of feedstock isn’t optimal or that the temperature has dropped too low.
7. Harvesting Biogas and Digestate
Once the system is running steadily, you’ll be able to collect the biogas from the gas outlet. At the same time, you will periodically need to remove the digestate—the nutrient-rich slurry remaining after digestion—which can be processed further into a usable fertilizer.
Action Step:
- Set up a safe storage solution for the biogas so you can use it when needed. This might be a simple storage bag or a more advanced gas cylinder system.
- Develop a schedule for periodically “bleeding off” the digestate. Use the liquid fraction on your fields as a fertilizer or evaluate if you need to compost the remaining solids further.
Maintenance and Safety: Keeping Your System Running Smoothly
Just like any farm equipment, an anaerobic digester requires regular maintenance to work well over the long term and stay safe. Here are some practical tips:
Regular Checks
- Daily/Weekly Inspections: Look at the tank seals, gas outlet, and feed inputs. Ensure there are no leaks or unusual smells (beyond what you expect from a natural process).
- Record Keeping: Maintain a log of feed amounts, temperature, pH, and gas output. Over time, these records can help you fine-tune the system for even better performance.
Temperature Control
Many digesters perform best at warm temperatures (often called the mesophilic range, around 30–40°C or 86–104°F). In colder months, you may need to insulate your digester or use a mild heating method to keep the process active.
- Action Step: Monitor the ambient temperature. Consider wrapping your digester with insulating materials or placing it in a sheltered area to keep it warm during winter.
Safety Measures
Biogas, though valuable, is flammable. Here’s how you can ensure safety:
- Proper Ventilation: The area around the digester and gas storage should be well-ventilated. Never store or use biogas in enclosed spaces where a leak could lead to dangerous build-ups.
- Regular Maintenance of Gas Lines: Check pipes and valves for wear or leaks. Replace any worn-out parts promptly.
- Training: Make sure that anyone working near or with the digester understands the basic safety protocols. Even simple training sessions can help prevent accidents.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Sometimes, you might notice a drop in gas production or a change in the odor of the digester. Most issues have simple fixes:
- If gas production dips, check the feedstock quality—maybe the mixture is too dry or too wet.
- If the pH level falls out of the optimal range, you might need to adjust the inputs by adding more of a balanced feed.
Keeping a calm, methodical approach to these challenges will not only protect your investment but also make your farm operations more resilient and self-reliant.
Financial and Environmental Benefits: More Than Just Savings
Cutting Operating Costs
Energy costs are rising, and relying on purchased fuels can be a significant drain on your farm’s budget. By producing your own biogas, you cut back on these expenses. Many farmers find that after the initial investment, the running costs of a well-maintained anaerobic digestion system are minimal compared to the benefits.
- Action Step: Calculate your potential savings. Keep records of current fuel costs and then compare these with the output of your biogas system to see how quickly your investment pays off.
Boosting Farm Profitability
Using digestate as a fertilizer can reduce or even eliminate the need to buy chemical fertilizers. Over time, the savings add up. Moreover, you might even have extra digestate or biogas to share with neighboring farms, paving the way for community-based energy networks or cooperative fertilizer sales.
Supporting a Greener Environment
Every farm that shifts to renewable energy sources like biogas contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Capturing methane that would otherwise escape from decomposing manure means you’re helping to lower the overall environmental impact of your farm. Cleaner air, improved soil health, and better water quality are just a few of the benefits that extend beyond your farm boundaries.
- Action Step: Consider joining local or regional sustainability programs. Some government grants or agricultural extension services offer support for farms investing in green technology, further reducing the risk of your initial investment.
Real-Life Example: A Farm’s Journey to Energy Independence
Let’s take a look at a practical example. Imagine a medium-sized dairy farm that struggled with manure management and high fuel costs for its operations. After researching anaerobic digestion, the farm owner decided to install a small digester.
Step 1: Planning and Setup The farmer started by recording the daily amount of manure produced. With the help of a local agricultural extension office, a simple and affordable digester was designed—using a repurposed concrete tank, a gas collection system, and basic monitoring tools.
Step 2: Trial and Adjustment During the trial phase, the farmer kept a daily log, noting the pH levels and gas output. When gas production was slow, a slight adjustment in the feed mix made a big difference. Gradually, the biogas output increased until the system stabilized, generating enough energy to power the farm’s milking parlor and heating system during winter.
Step 3: Reaping the Benefits Within a year, the farmer reported a significant reduction in fuel costs and a noticeable improvement in crop yields on fields fertilized using the digestate. The system not only managed waste more efficiently but also turned out to be a profitable investment, with the added benefit of a cleaner environment around the farm.
Farmers considering a switch to anaerobic digestion can draw many lessons from this story: start small, keep careful records, and don’t be afraid to adjust the process as you learn more about your specific feedstock and conditions.
Practical Checklist: Steps to Get Started
Before diving headfirst into an anaerobic digestion project, it’s useful to have a checklist that sums up the key actions:
- Evaluate Your Waste Sources:
- Gather data on the types and volume of organic waste produced daily or seasonally.
- Consult with local agricultural extension services or sustainability groups.
- Decide on the System Scale:
- Choose between a pilot project or a larger, full-scale installation based on your resources.
- Research different digester designs and decide which fits your farm best.
- Plan the Build or Purchase:
- Source a reliable, airtight tank, piping, and gas collection system.
- If constructing your own, gather advice from experienced farmers or local experts.
- Set Up Monitoring Tools:
- Invest in a thermometer, pH meter, and a logbook for routine checks.
- Be flexible and ready to tweak feeds or insulation based on seasonal changes.
- Implement Safety Measures:
- Install proper ventilation around the digester and storage areas.
- Regularly inspect pipes, valves, and seals. Ensure everyone on the farm knows basic safety procedures.
- Start Slowly and Monitor:
- Begin with small batches of feedstock.
- Gradually adjust when comfortable with the system’s performance, always keeping detailed records.
- Leverage Available Support:
- Look into government grants, local cooperative programs, or advice from neighboring farms with similar systems.
- Share your experiences and learn from others in the farming community.
- Assess Financial Viability:
- Calculate initial investments versus long-term savings on energy and fertilizers.
- Reinvest part of the savings into improving and expanding the system over time.
This checklist can serve as your roadmap to transform your farm waste into both renewable energy and high-quality fertilizer.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Farming and Sustainable Energy
The push towards sustainability is more than just a trend—it’s becoming a way of life in modern farming. As energy costs continue to climb and environmental concerns grow, investing in technologies like anaerobic digestion not only makes economic sense but also positions your farm as a community leader in sustainable practices.
In the future, we can expect:
- More Cooperative Projects: Farms might join forces to build larger, cooperative digestion systems that serve multiple fields or even entire farming communities. Sharing resources and the benefits of renewable energy can strengthen local networks and boost resilience against external market pressures.
- Improved Technology and Ease of Use: As more farmers adopt anaerobic digestion, expect to see improvements in design, monitoring, and user-friendliness of the systems. This will make it easier for even small-scale or beginning farmers to jump on board with the technology.
- Expanded Support and Incentives: Many regions are already offering grants and technical assistance to encourage renewable energy projects. Keeping an eye on these opportunities can help defray initial costs and provide additional expertise during the setup phase.
Conclusion: Your Next Steps to a Greener, More Profitable Farm
Anaerobic digestion presents a unique opportunity to turn everyday farm waste into valuable resources—renewable energy and nutrient-rich fertilizer—all while improving your farm’s environmental footprint. You now have a clear, step-by-step guide on what anaerobic digestion is, how it works, and how you can set up and maintain your own system.
Take a moment to evaluate the resources on your farm. Ask yourself:
- Do you have enough organic waste to fuel a small energy project?
- Could the savings on fuel and fertilizer help pay off an initial investment in the system?
- Are there local experts, grants, or farmer cooperatives that can help you take the next step?
If the answers lean toward “yes,” it might be time to seriously consider anaerobic digestion. Start small, experiment, and adjust as you learn. Before you know it, you’ll be generating your own renewable energy, reducing waste, and ensuring that every part of your farm contributes to a sustainable cycle.
Remember, every farm is unique, and the transition to using renewable energy is a journey. But with clear planning, routine checks, and a bit of patience, the rewards can be tremendous both for your farm’s bottom line and for the environment.
Additional Resources to Explore
- Local Agricultural Extension Services: Many counties and states have extension services that can offer hands-on advice, technical assistance, and even demonstration projects on anaerobic digestion technology.
- Farmer Cooperatives and Renewable Energy Grants: Look into cooperative projects or grants available in your region. These can provide financial support or shared learning experiences with other local farms.
- Workshops and Field Days: Attend local workshops or field days on renewable energy in agriculture to see working systems, ask questions, and get the feel of how a fully operating digester works in real-life conditions.
- Online Communities and Forums: Joining online groups of farmers focusing on sustainable practices will help you share tips, troubleshoot issues, and stay updated on new developments in anaerobic digestion.
By following these guidelines and practical steps, you can harness the natural power of anaerobic digestion to create a cleaner, more efficient, and economically beneficial farming operation. The future of farming is moving towards sustainability and self-reliance, and anaerobic digestion is one of the key tools to help you get there.
Embrace the process, adapt it to your needs, and soon you may find that waste is no longer a problem but rather a valuable resource that fuels your farm’s growth and success.